Learn what PTSD is, its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments. Discover how early intervention and support can help manage PTSD.
Table of Contents
Toggle
What is PTSD?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety-related condition that may develop after an individual has been exposed to a traumatic event that posed a serious threat to their safety or life. While it’s natural to experience fear during and after a traumatic situation, PTSD occurs when these intense feelings of fear and distress persist long after the event has ended, affecting a person’s daily functioning.
Research says that People suffering from PTSD might encounter persistent symptoms such as recurring nightmares, invasive thoughts, or extreme anxiety. Recognizing PTSD as a legitimate and treatable mental health issue is crucial.
If you are experiencing these symptoms, reach out to our psychologists for support and guidance.

PTSD Full Form
The PTSD full form in medical terminology is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. This condition is classified as a serious mental health disorder triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Understanding the full form of PTSD helps in recognizing its significance in medical contexts, making it easier for individuals to seek appropriate care.
What are the Causes of PTSD?
PTSD can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. According to research, Common causes of PTSD include:
Assault:
Physical or sexual assault can deeply traumatize individuals, leading to profound anxiety and a sense of isolation, akin to symptoms observed in Social Anxiety. disorders.
Military Exposure:
Service members may develop PTSD from harrowing experiences in combat, where exposure to intense violence and the trauma of loss can linger.Severe Accidents:
Traumatic accidents, like vehicle crashes or major workplace incidents, can imprint vivid memories that intrude on an individual’s daily life, precipitating PTSD.Natural Disasters:
The chaos and threat to life associated with natural disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes can profoundly impact mental health, potentially leading to PTSD.Sudden Loss of a Loved One:
The abrupt death of someone close can shock one’s emotional system, sometimes leading to prolonged grief that evolves into PTSD.
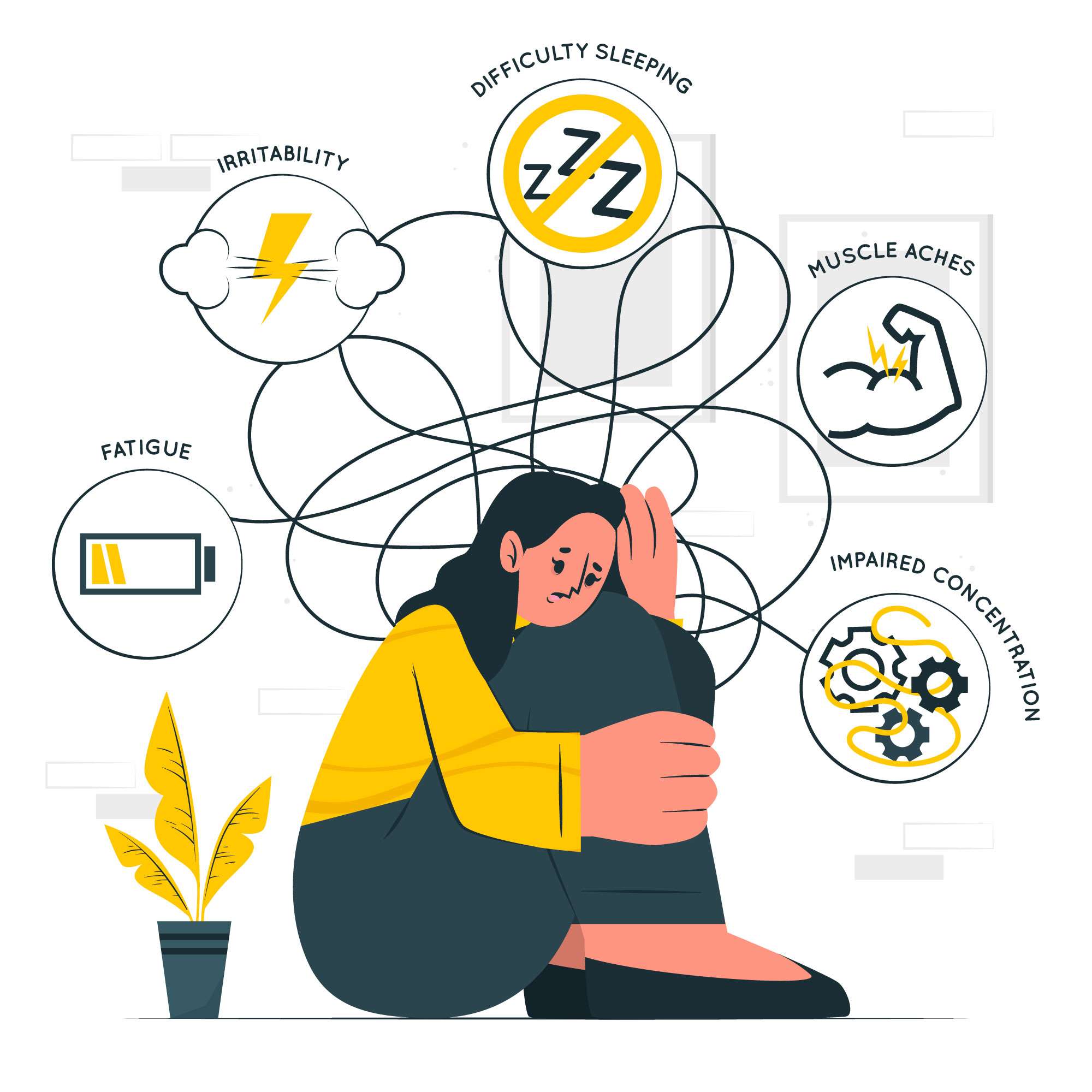
What are the Symptoms of PTSD?
PTSD can manifest in various ways, and symptoms may vary from person to person. Common symptoms of PTSD include:
Flashbacks and Recurrent Memories:
Individuals may relive the trauma through flashbacks or dreams, feeling as though the event is occurring again.Avoidance:
There may be a deliberate avoidance of reminders of the trauma, such as specific locations or activities that trigger painful memories.Hyperarousal:
Constant alertness and expecting danger can lead to hypersensitivity to sounds, difficulty sleeping, and irritability.Mood and Thought Change:
Feelings of detachment or estrangement from others, persistent negative thoughts about oneself or the world, and diminished interest in previously enjoyed activities are common.Emotional Numbness:
This involves a significant detachment from emotional experiences, whether positive or negative, appearing aloof or distant to others.Reactivity:
An exaggerated response to triggers that recall the traumatic event, such as panic when hearing loud noises or experiencing intense anxiety in crowded spaces.
These symptoms can be distressing and disruptive to daily life, affecting relationships, work, and overall well-being.
If you find yourself struggling with these symptoms, contact our psychologists for professional assistance.
PTSD ICD-10
The PTSD ICD-10 code is F43.1, and it is used to classify Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder under the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). This coding system is essential for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating PTSD accurately, ensuring proper documentation and treatment planning.

How can you Prevent PTSD?
While it’s not always possible to prevent PTSD after experiencing trauma, certain strategies can reduce the risk or mitigate its impact:
Prompt Support:
One effective approach to potentially preventing PTSD is to offer immediate support following a traumatic incident. Quick access to a counselor or therapist right after the event can significantly help individuals manage their emotions more effectively. Such prompt intervention can decrease the likelihood of developing PTSD by providing necessary guidance to help them cope with and understand their experiences, thus reducing the trauma’s overwhelming impact.Enhancing Resilience:
Strengthening resilience is another crucial preventative strategy for PTSD. Resilience involves fortifying oneself internally to better withstand stress and adversity. Engaging in mindfulness exercises, maintaining a regular physical activity regimen, and cultivating strong relationships with family and friends can all contribute to building this inner strength. Well-developed coping strategies and robust social networks can improve one’s ability to navigate traumatic experiences, potentially reducing the trauma’s long-term mental health effects.Active Support Seeking:
Encouraging individuals to actively seek support is also beneficial. Engaging in conversations with supportive friends and family or consulting mental health professionals can make a significant difference. The presence of a supportive network ensures that one does not face their stressors and fears alone, which is instrumental in mitigating the risks of developing PTSD. Awareness that there is a supportive community available can help individuals manage their response to trauma more effectively.Increasing Awareness and Education:
It is vital to educate individuals about PTSD and its symptoms. Understanding and recognizing the early signs of PTSD in oneself or others can prompt earlier intervention, preventing the condition from exacerbating. Informing individuals and communities about PTSD equips them to better support each other and seek timely help, reducing the probability of PTSD following traumatic events.
How to Diagnose PTSD?
Diagnosing PTSD involves a thorough assessment by a qualified mental health professional. The diagnosis typically includes the following steps:
Clinical Interview:
The diagnostic process begins with a detailed clinical interview by a mental health professional. This interview allows the clinician to gather in-depth information about the individual’s symptoms, personal history, and trauma experiences. This discussion is vital as it lays the groundwork for an accurate diagnosis by providing crucial insights into the individual’s psychological state.Applying Diagnostic Criteria:
The clinician uses the ICD-10 or DSM-5 diagnostic criteria, which outline specific symptoms triggered by a traumatic event, like recurring flashbacks and avoidance behaviors.Utilization of Assessment Tools:
Mental health professionals may also use various psychological assessment instruments to measure the severity of PTSD symptoms. These tools, which include questionnaires and standardized scales, aid in quantifying the impact of the symptoms on daily functioning, providing a clearer picture of the severity of the condition.Exclusion of Other Conditions:
Finally, the clinician must rule out other possible mental health disorders or medical conditions that could be responsible for the symptoms, ensuring that disorders such as anxiety, depression, or brain injuries are not confused with PTSD. This step is essential for a precise diagnosis tailored to the individual’s specific situation.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and support for individuals with PTSD.
What are the Complications of PTSD?
Research says that Untreated or poorly managed PTSD can lead to various complications that impact mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Some complications associated with PTSD include:
Mood Disorders:
Continuous exposure to stress and emotional disturbances due to PTSD can deteriorate mental health, potentially leading to conditions like depression or generalized anxiety disorder. Over time, these can evolve into more serious mental health issues requiring concurrent management with PTSD.Substance Use:
It’s not uncommon for those suffering from PTSD to turn to alcohol or drugs as a temporary escape from their symptoms. Unfortunately, this coping mechanism can develop into a substance use disorder, complicating PTSD treatment and impacting overall health.Social and Relationship Challenges:
PTSD symptoms such as emotional detachment, social withdrawal, and heightened irritability can impair personal relationships. Individuals may become distant or overreact in social interactions, leading to conflicts and strained relationships.Workplace Difficulties:
Symptoms like difficulty concentrating, irritability, and avoidance can hinder professional performance, potentially leading to job insecurity or unemployment. The additional stress from these work-related problems can exacerbate PTSD symptoms.Physical Health Deterioration:
Chronic stress from PTSD can manifest physically, potentially causing cardiovascular problems, gastrointestinal issues, or a compromised immune system, all of which necessitate further medical intervention.Risk of Suicide:
Severe cases of PTSD might lead to suicidal thoughts or actions, particularly if accompanied by profound depression. Immediate and effective intervention is crucial to mitigate these risks and provide support.
Addressing these complications requires comprehensive treatment that addresses both PTSD symptoms and any co-occurring conditions.

What are the Treatment Options for PTSD?
Effective treatment options are available to help individuals manage and recover from PTSD. Common treatments include:
Psychotherapy:
Approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Exposure Therapy, and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) are effective in treating PTSD.Medication:
Certain post traumatic stress disorder drugs, including antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications, help alleviate symptoms. These post traumatic stress disorder medications are often used alongside therapy for best results.Support Groups:
These groups provide vital social support, connecting individuals with peers who have similar experiences. They offer a platform for sharing coping strategies and receiving emotional support, contributing to a sense of community and reduced isolation.Lifestyle Modifications:
Incorporating stress-reduction practices like mindfulness, regular physical activity, and proper sleep hygiene can significantly benefit those managing PTSD, enhancing both mental and physical well-being.Educational Workshops:
Workshops aimed at educating individuals about PTSD can demystify the condition and introduce effective coping strategies. These sessions provide crucial knowledge and tools that help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively.
If you are going through a tough time and need someone to talk to, we are here for you. Reach out to us for a heartfelt chat or a comforting call with one of our caring psychologists. You are not alone in this journey, we are always here for you.